Veganism is on the rise, and you might wonder why. It’s not just about healthy eating—it’s about overall well-being and ethical choices. Vegan diets focus on plant-based foods like fruits, vegetables, and dairy alternatives, avoiding meat and animal products. Studies show that a vegan diet can lower the risk of heart disease, prevent type 2 diabetes, and reduce animal cruelty. In this guide, we’ll cover essential points to help you start your vegan journey.
What is Veganism?
Veganism is more than just a diet; it’s a lifestyle choice that involves excluding all animal products. Vegans avoid eating any food that comes from animals, such as meat, dairy, eggs, and honey. Many vegans also avoid using products made from animals, like leather, fur, and cosmetics that are tested on animals.
While veganism is similar to vegetarianism, vegans take it a step further by eliminating all animal-derived ingredients, whereas vegetarians might still consume eggs, milk, and honey. Veganism is a plant-based lifestyle that centers around fruits, vegetables, grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds.
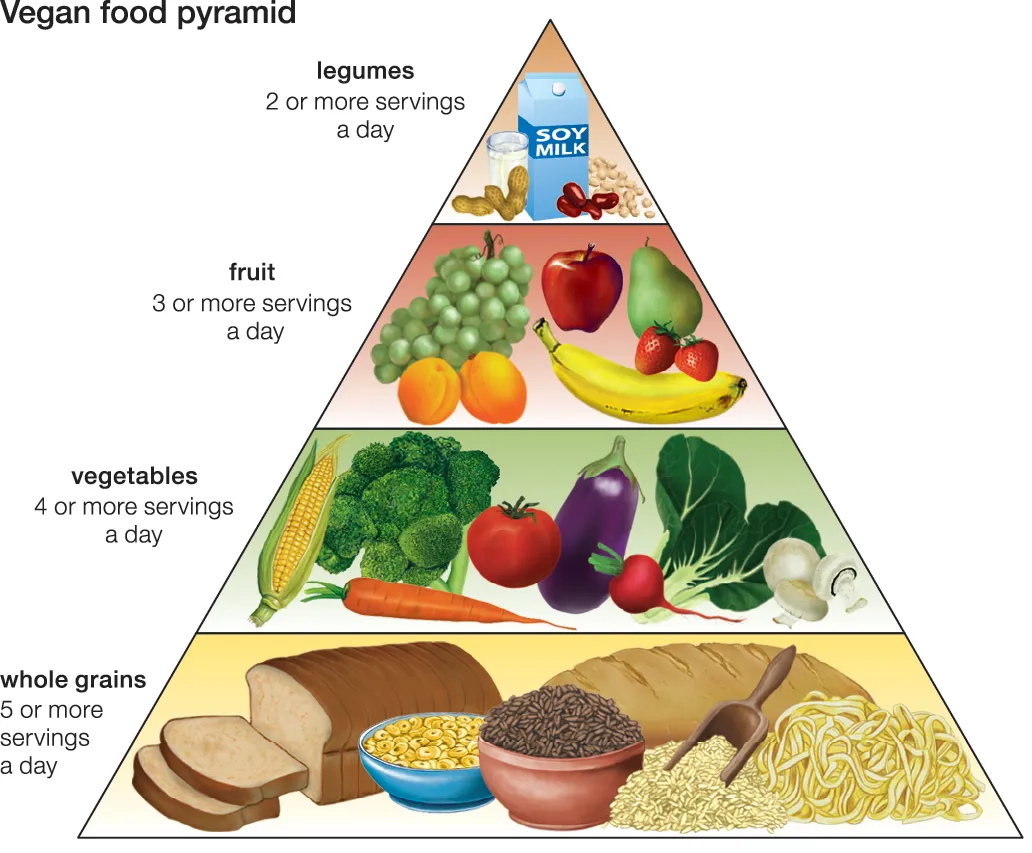
The Vegan Food Pyramid
Curious about what vegans eat? The Vegan Food Pyramid helps outline a balanced vegan diet.
- Base:Whole grains like oats, rice, and bread for energy and fiber.
- Next Level: Vegetables and fruits, essential for vitamins and nutrients.
- Middle: Legumes, nuts, and seeds, which are rich in protein and healthy fats.
- Top: Plant-based oils like olive oil and fortified foods like plant milk, which provide calcium and vitamin B12.
Following this pyramid ensures a balanced and nutritious vegan diet.
Why Go Vegan?
- Health Benefits:
Studies have shown that a vegan diet can help lower cholesterol levels, reduce the risk of heart disease, and support weight management. Vegan diets are naturally rich in fiber, vitamins, and antioxidants, which can promote better digestion and overall health. - Environmental Impact:
Plant-based diets have a significantly lower environmental footprint compared to diets that include animal products. By choosing vegan options, you reduce water usage, greenhouse gas emissions, and deforestation, all of which contribute to environmental sustainability. - Ethical Considerations:
Many people choose veganism out of concern for animal welfare. By not consuming animal products, vegans actively take a stand against practices like factory farming, animal testing, and cruelty in the production of food and goods.
Health Benefits of a Vegan Diet
Adopting a vegan diet can have a profound impact on your health. Here are some of the key benefits:
- Improved Heart Health:
A vegan diet is typically lower in saturated fats, which can help reduce cholesterol levels and lower the risk of heart disease. Plant-based diets also tend to be high in fiber, which supports cardiovascular health by improving blood circulation and regulating cholesterol. - Lower Risk of Type 2 Diabetes:
Research shows that people who follow plant-based diets have a reduced risk of developing type 2 diabetes. The high fiber content of vegan diets helps regulate blood sugar levels and improves insulin sensitivity. - Weight Management:
Vegan diets can be effective for maintaining a healthy weight. Plant-based foods tend to be lower in calories and higher in fiber, helping you feel full without consuming excess calories. This can be particularly beneficial for those looking to lose or manage weight without restricting portion sizes. - Digestive Health:
The high fiber content in fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains supports a healthy digestive system. A plant-based diet can help prevent constipation and promote regular bowel movements, improving overall gut health. - Reduced Cancer Risk:
Some studies suggest that a vegan diet may lower the risk of certain types of cancer, particularly colon and breast cancer. This is largely due to the high antioxidant levels found in plant-based foods, which help protect the body from cell damage.
Can Vegans Get All the Nutrients They Need?
Yes, a well-planned vegan diet provides all the necessary nutrients. Plant-based foods such as fruits, vegetables, grains, and legumes are packed with vitamins, minerals, and fiber. Protein is easily sourced from foods like beans, lentils, tofu, and tempeh.
Some nutrients, like vitamin B12 and iron, may require extra attention. B12 is found mainly in animal products, so vegans often take fortified foods or supplements. With a bit of planning, a vegan diet can meet all your nutritional needs.
Can Vegan Food Provide Enough Protein?
Absolutely! Plant-based proteins like beans, lentils, chickpeas, tofu, and quinoa are excellent sources. For example, a cup of lentils offers about 18 grams of protein. By including these in your meals, you can meet your protein needs without relying on animal products.
Examples of high-protein vegan foods:
- Black Beans (15g per cup, cooked)
- Edamame (17g per cup, cooked)
- Tempeh (21g per 1/2 cup)
- Seitan (25g per 3 oz)
- Peas (9g per cup, cooked)
- Hemp Seeds (10g per 3 tablespoons)
- Almonds (6g per ounce)
- Pumpkin Seeds (9g per ounce)
- Chia Seeds (4g per 2 tablespoons)
- Peanut Butter (8g per 2 tablespoons)
- Sunflower Seeds (6g per ounce)

How Easy is It to Prepare Vegan Food?
Preparing vegan food is often quick and simple, making it easy to maintain a plant-based diet. Many vegan meals, like salads, stir-fries, and smoothies, can be made in just minutes using fresh ingredients. There are also convenient, ready-made plant-based proteins like tofu and tempeh that save time and add variety to your meals. Whether you’re cooking from scratch or using store-bought options, vegan meals can be both easy to prepare and nutritious. Here’s a great example of a simple yet delicious vegan recipe:
Recipe: Chickpea and Sweet Potato Curry
Total Time: 30-40 minutes, Servings: 4
Ingredients:
- 1 large sweet potato (peeled and chopped into cubes)
- 1 can (400g) of chickpeas (drained and rinsed)
- 1 can (400ml) of coconut milk
- 1 can (400g) of diced tomatoes
- 1 medium onion (finely chopped)
- 2 cloves garlic (minced)
- 1 tbsp curry powder
- 1 tsp ground cumin
- 1/2 tsp turmeric powder
- 1 tsp grated fresh ginger (or 1/2 tsp ground ginger)
- 1 tbsp olive oil or coconut oil
- Salt and pepper to taste
- Fresh cilantro for garnish (optional)
- Cooked rice or quinoa (for serving)
Procedure:
- Prepare the ingredients:
Peel and chop the sweet potato into small cubes. Drain and rinse the chickpeas, and chop the onion and garlic. - Cook the sweet potato:
In a large pot, add the cubed sweet potato and enough water to cover. Bring to a boil and cook for about 10-15 minutes, or until tender. Drain and set aside. - Sauté the aromatics:
In the same pot, heat the olive oil or coconut oil over medium heat. Add the chopped onion, garlic, and grated ginger. Sauté for 3-5 minutes until the onion becomes translucent. - Add the spices:
Stir in the curry powder, cumin, and turmeric, cooking for another 1-2 minutes until the spices become fragrant. - Add the liquids:
Pour in the canned coconut milk and diced tomatoes. Stir everything together and bring the mixture to a simmer. - Add the sweet potato and chickpeas:
Gently fold in the cooked sweet potato cubes and chickpeas. Let the curry simmer for 10 minutes, allowing the flavors to meld together. Season with salt and pepper to taste. - Garnish and serve:
Once the curry is done, remove it from the heat and garnish with fresh cilantro if desired. Serve the curry over cooked rice or quinoa for a complete, filling meal.
Nutritional Benefits:
- Sweet Potato: Rich in vitamins A and C, fiber, and antioxidants, supporting immune function and eye health.
- Chickpeas: High in plant-based protein and fiber, keeping you full and aiding digestion.
- Coconut Milk: Adds creaminess and healthy fats, contributing to brain function and energy.
- Spices: Provide anti-inflammatory benefits and boost metabolism.
This chickpea and sweet potato curry is not only easy to make but also nutritious, filling, and packed with flavor. It’s a perfect meal for lunch or dinner and can be stored for leftovers, making it ideal for busy weekdays.






Comments are closed.